数字三角形–动态规划
题目
有一个由非负整数组成的三角形,第一行只有一个数,除了最下行之外每个数的左下方和右下方各有一个数,如下图:
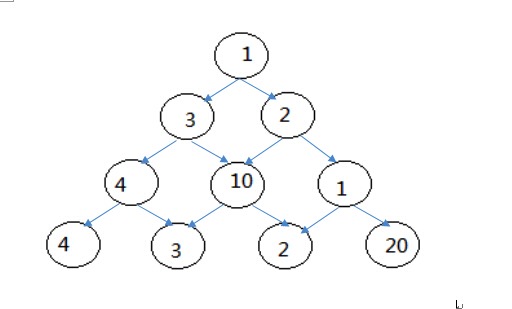
从第一行开始,每次可以往做下或右下走一格,直到走到最下行,把沿途经过的数全部加起来,如何走才能使得这个和最大。
分析
可以从下往上来分析
如下:
1
3 2
4 10 1
4 3 2 20
从下开始往上更新。
第1次更新为:
1
3 2
8 13 21
4 3 2 20
第2次更新:
1
16 23
8 13 21
4 3 2 20
第3次更新:
24
16 23
8 13 21
4 3 2 20
三种实现方法:递归、递推、记忆化搜索
/*
递归
4
1
3 2
4 10 1
4 3 2 20
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int [][]a = new int [100][100]; //用来存储数字三角形的数据
static int [][]c = new int [100][100]; //用来存路径
static int n ;
static int count;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scanner.nextInt();
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
for(j=0;j<=i;j++){
a[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println(fun(0, 0));
System.out.println("计算了"+count+"次");
//输出走的路径
System.out.print("路径如下:(0,0)");
int t = 0;
for(i=1;i<n;i++){
System.out.print("->("+i+","+c[i-1][t]+")");
t = c[i-1][t];
}
}
public static int fun(int i,int j){
if(i == n-1)
return a[i][j]; //如果到了最下面一层,就返回当前这个数
count++;
int t1 = fun(i+1, j);
int t2 = fun(i+1, j+1);
if(t1>t2){
c[i][j] = j; //表示当前这个位置是从下一行哪个数据来的
return a[i][j]+t1;
}else {
c[i][j] = j+1; //表示当前这个位置是从下一行哪个数据来的
return a[i][j]+t2;
}
//return a[i][j] + Math.max(fun(i+1, j), fun(i+1, j+1));
}
}
/*
* 递推
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int [][]a = new int [4][4];
static int [][]d = new int [4][4];
static int n ;
static int count;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scanner.nextInt();
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
for(j=0;j<=i;j++){
a[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
d[i][j] = a[i][j];
}
}
for(i=n-1;i>=1;i--){
for(j=0;j<i;j++){
count++;
d[i-1][j]+=Math.max(d[i][j], d[i][j+1]);
}
}
System.out.println(d[0][0]);
System.out.println("计算了"+count+"次");
}
}
/*
* 记忆化搜索
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int [][]a = new int [100][100];
static int [][]d = new int [100][100];
static int n ;
static int count;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scanner.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++){
a[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println(fun(0, 0));
System.out.println("计算了"+count+"次");
}
public static int fun(int i,int j){
if(i == n-1)
return a[i][j]; //如果到了最下面一层,就返回当前这个数
if(d[i][j]!=0) return d[i][j];
count++; //统计 计算了多少次
d[i+1][j] = fun(i+1, j);
d[i+1][j+1] = fun(i+1, j+1);
return a[i][j] + Math.max(d[i+1][j], d[i+1][j+1]);
}
}
